ARTICLE
Solar Panel Foundations in Australia's Diverse Soils

Summary
- This article provides a technical comparison of foundation options for ground-mounted solar panels in Australia.
- It details the challenges presented by common Australian soil types, including reactive clay, sandy, and rocky ground.
- The primary focus is a comparative analysis of concrete ballast, driven piles, ground screws, and helical piles.
- Data tables and graphs are used to illustrate performance metrics like installation speed, load capacity, and site impact.
- Helical piles are presented as a highly effective and versatile solution for many Australian solar farm projects.
Understanding Australian Soil Profiles for Solar Farm Development
This section will discuss the unique geological landscape of Australia and why a one-size-fits-all approach to solar panel foundations is inadequate. It will emphasise the necessity of a thorough site assessment.
Common Australian Soil Types and Their Engineering Challenges
A paragraph-based description of the prevalent soil conditions across Australia. Focus on the engineering properties that impact foundation design. Cover reactive clays (common in the eastern states), sandy soils (prevalent in Western Australia and coastal regions), and the challenges of rocky or mixed-profile grounds found nationwide. This section will set the stage for why foundation selection is so critical.
The Importance of Geotechnical Investigations
This sub-section will explain the role of a geotechnical report in solar farm development. It will detail what engineers should look for in a soil test, such as soil bearing capacity, reactivity, and depth to bedrock. This reinforces the technical nature of the article and highlights best practices for the target audience. Keywords: soil testing for solar projects, geotechnical requirements.
Comparative Analysis of Solar Panel Foundation Systems
This core section will compare the four main types of ground mount solar foundations used in Australia. Each foundation type will be discussed in its own subsection using paragraphs, outlining its methodology, pros, and cons from an engineering perspective.
Concrete Ballast and Slab Foundations
Discussion on the use of concrete footings, their high material requirement, significant site disturbance, and long curing times. Mention their suitability for sites with shallow rock or where excavation is restricted.
Driven Pile Foundations
Explanation of how driven piles (like I-beams) are installed through vibration or impact. Discuss their effectiveness in certain soils but also the risks of pile refusal in rocky ground and the significant noise and vibration during installation.
Ground Screw Foundations
An overview of ground screws, highlighting their similarity to helical piles but with different applications. Discuss their speed of installation but also their limitations in dense or rocky soils compared to the more robust design of a helical pile.
Helical Pile Foundations
Detailed explanation of helical piles (also known as screw piles). Describe their installation process using torque, which minimises site disturbance and vibration. Emphasise their design, which allows for immediate loading and verifiable capacity through torque correlation.
| Feature | Concrete Ballast | Driven Piles | Ground Screws | Helical Piles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Speed | Slow (excavation, curing) | Fast | Very Fast | Very Fast |
| Site Disturbance | High (excavation, spoil) | Moderate (vibration) | Low | Very Low (no spoil) |
| Load Capacity | High | High | Moderate-High | Very High (verifiable) |
| Soil Suitability | Versatile but costly | Good in clays/sands | Best in soft/medium soils | Excellent in most soils |
| Vibration/Noise | Low (during pour) | High | Low | Very Low |
| Removability | Difficult | Moderate | Easy | Easy |
| Cost | High (materials, labour) | Moderate | Moderate | Cost-Effective |
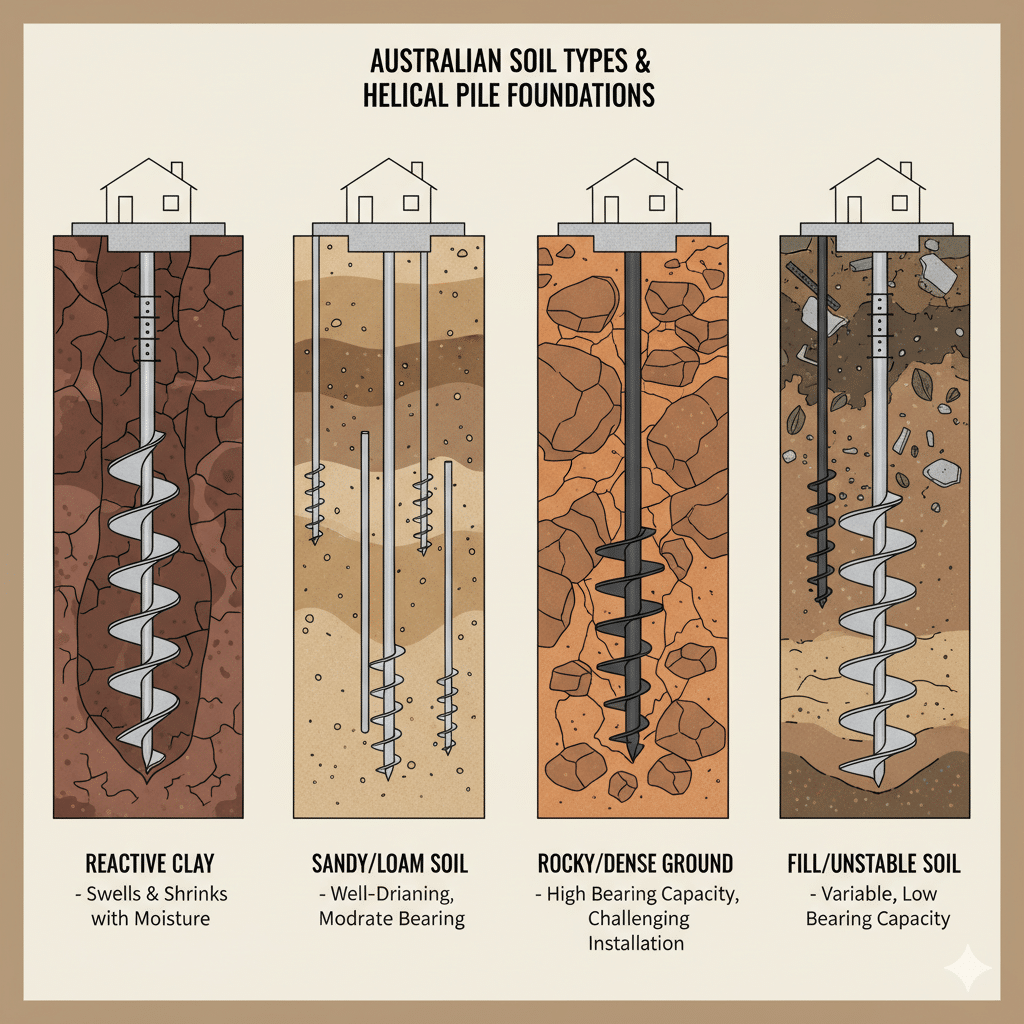
Performance Matrix: Helical Piles in Varied Australian Soils
This section will focus exclusively on the performance of helical piles, linking back to the soil types discussed earlier. It will use data to substantiate claims of versatility and reliability.
Performance in Reactive Clay Soils
Explain how the helical design anchors the pile below the zone of seasonal moisture change, mitigating the risks of uplift and movement associated with Australia’s reactive clays. This is a significant advantage for engineers designing for long-term stability.
Performance in Sandy and Loamy Soils
Discuss how helical piles provide excellent tension and compression resistance in sandy soils by transferring the load to the helical plates, which act as bearing elements in less cohesive ground.
Performance in Rocky and Difficult Ground Conditions
Address the misconception that screw piles are unsuitable for hard ground. Explain how advanced installation techniques and pile design allow heical piles to be installed in dense, rocky soils where driven piles might meet refusal.
| Soil Type | Key Engineering Challenge | Helical Pile Advantage | Installation Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactive Clay | Soil Heave/Subsidence | Anchors below reactive zone | Torque monitoring ensures stability |
| Sandy/Loamy Soil | Lower Bearing Capacity | Helices provide broad bearing surface | Pile diameter & helix config is key |
| Rocky/Dense Ground | Installation Refusal | Can penetrate/navigate difficult strata | Requires high-torque drive heads |
| Fill/Unstable Soil | Unpredictable Settlement | Extends to competent load-bearing soil | Depth can be easily adjusted on site |
Key Engineering Advantages of Helical Piles for Australian Solar Projects
This section will synthesise the information and present a clear argument for why helical piles are often the superior choice.
Accelerated Project Timelines
Focus on the speed of installation. Helical piles can be installed and loaded on the same day, drastically reducing construction schedules compared to the curing time required for concrete. This is a major commercial advantage.
Minimal Site Disturbance and Environmental Compliance
Discuss the low-impact nature of the installation. No excavation spoil, minimal vegetation clearing, and low noise levels make helical piles ideal for environmentally sensitive areas or sites near residential zones.
Real-Time Load Capacity Verification
This is a key technical benefit for engineers. Explain the principle of torque correlation, where the installation torque provides a direct indication of the pile’s load-bearing capacity, offering immediate and reliable quality assurance on site.
Adaptability to Remote and Undulating Terrains
Highlight the logistical advantages. The equipment for installing helical piles is often smaller and more agile than that for concrete or driven piles, making it perfect for remote Australian sites with challenging access or uneven ground.
Summary On Solar Panel Foundations
In summary, selecting the best foundation for solar panels in Australia requires a careful analysis of site-specific geotechnical data. While traditional methods have their place, the engineering advantages of helical piles are compelling.
Their rapid installation, minimal environmental impact, and verifiable performance make them a highly adaptable and efficient solution for navigating Australia’s diverse soil conditions.
For engineers aiming to optimise project timelines, costs, and long-term stability, helical piles present a robust and modern foundation choice for solar farm construction.
Frequently Asked Questions About Solar Panel Foundations
What Is the Best Base for Ground-Mounted Solar Panels?
The best base depends on a geotechnical investigation of the site. However, helical piles are often considered the superior choice in many Australian conditions due to their versatility across clay, sandy, and even rocky soils, combined with their rapid installation and minimal site disturbance.
How Deep Should Footings Be for Solar Panels?
Footing depth is determined by several factors, including the soil’s bearing capacity, frost line (less of a concern in most of Australia), and wind load calculations according to AS/NZS 1170.2. For helical piles, the depth is determined by the point at which the pile reaches a competent load-bearing stratum and the required installation torque is achieved, which could be anywhere from 1.5 to 10 metres or more.
Can You Put Solar Panels on Clay Soil?
Yes, but special considerations are needed for Australia’s highly reactive clays. Foundations must be designed to resist movement from soil swelling and shrinking. Helical piles are an excellent solution as they can be installed deep enough to anchor below this reactive zone, ensuring the stability of the solar array.
What Type of Foundation Is Used for Solar Power Plants?
Solar power plants in Australia use several foundation types, including concrete ballasts, driven piles, ground screws, and helical piles. The choice is dictated by soil conditions, project scale, environmental constraints, and budget. Helical pile and driven pile systems are increasingly popular for large-scale projects due to their speed.
Do Ground-Mounted Solar Panels Need a Concrete Base?
No, a concrete base is not the only option. Systems like helical piles, ground screws, and driven piles are “concrete-free” foundations. These alternatives offer significant advantages in terms of installation speed, reduced environmental impact, and ease of decommissioning.
How Do You Anchor Solar Panels to the Ground Without Concrete?
You can anchor solar panels without concrete using geotechnical foundations like helical piles or ground screws. These are screwed directly into the ground using hydraulic machinery. The helical plates on the pile provide the necessary bearing and uplift resistance to secure the solar racking system against gravity and wind loads.
Need a quote or more info? Start here.
Contact Us
info@helicalpilesaustralia.com.au
+61 2 7251 9258
Mon–Fri, 8:00am–5:00pm AEST

Built for complexity.
Engineered for certainty.
A trusted partner for large-scale energy and infrastructure projects where precision isn’t optional, it’s mandatory
© 2025 Helical Piles Australia. All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
info@helicalpilesaustralia.com.au
+61 2 7251 9258
Mon – Fri, 8:00am – 5:00pm AEST
Location
Ground Floor 3, 189 Kent St
Sydney, NSW 2000

